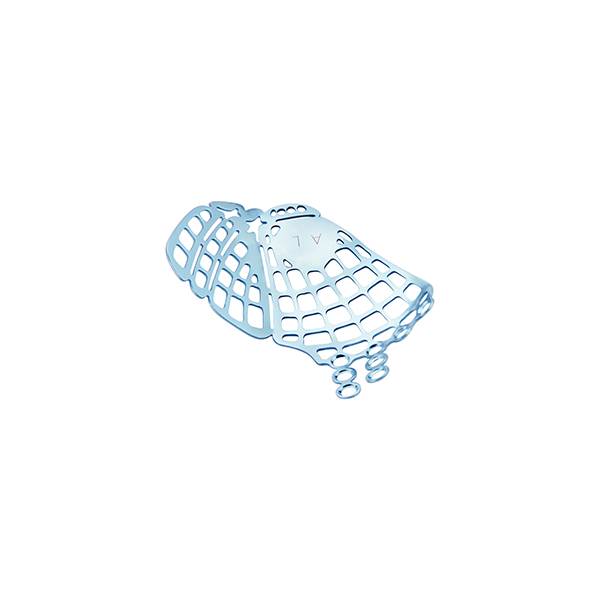
Material: medical pure titanium
Product specification
|
Thickness |
Item No. |
Specification |
|
|
0.4mm |
12.09.0411.303041 |
left |
30*30mm |
|
12.09.0411.303042 |
right |
||
|
0.5mm |
12.09.0411.303001 |
left |
|
|
12.09.0411.303002 |
right |
||
|
Thickness |
Item No. |
Specification |
|
|
0.4mm |
12.09.0411.343643 |
left |
34*36mm |
|
12.09.0411.343644 |
right |
||
|
0.5mm |
12.09.0411.343603 |
left |
|
|
12.09.0411.343604 |
right |
||
Features & Benefits:
• according to the anatomy of the orbital floor and orbital wall structure design, effectively avoid the optic hole and other important structures
• anatomy, lobulated design, as far as possible to reduce the workload of shaping, effectively restore the orbital cavity bone continuity, saves the operation time, reduce the surgical trauma, less postoperative complications.
• lower orbital wall is as thin as paper, therefore, retain the hard area in the rear of orbital floor titanium mesh. Help reset the incarcerated eyeball tissue and fat, restore the orbital cavity volume and eye movements, improve eye subsidence and diplopia.
Matching screw:
φ1.5mm self-drilling screw
Matching instrument:
cross head screw driver: SW0.5*2.8*75/95mm
straight quick coupling handle
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket. The volume of the orbit in the adult human is 30 millilitres, eye occupies 6.5 ml of total. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, check ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.
The orbits are conical shape or four-sided pyramidal cavities, open into face midline and point back into the head. A base, an apex and four walls make up each orbit.
Bony walls of the orbital canal in humans is a mosaic of seven embryologically distinct structures, consist of the zygomatic bone laterally, the sphenoid bone, with its lesser wing forming the optic canal and its greater wing forming the lateral posterior portion of the bony orbital process, the maxillary bone inferiorly and medially which, along with the lacrimal and ethmoid bones, forms the medial wall of the orbital canal. The ethmoid air cells are extremely thin, and form a structure known as the lamina papyracea, the most delicate bony structure in the skull, and one of the most commonly fractured bones in orbital trauma.
The lateral wall is formed by the frontal process of zygomatic and more posteriorly by the orbital plate of the greater wing of sphenoid. The bones meet at the zygomaticosphenoid suture. The lateral wall is the thickest wall of the orbit, it is the most exposed surface, so easier to encounter highly vulnerable to blunt force trauma.
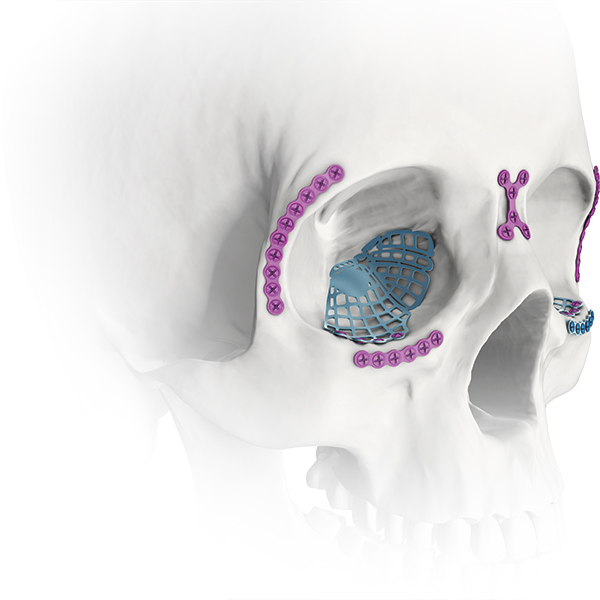
Inferior orbital wall fracture is the most common fracture in orbital blowout fracture, which often causes complications such as enophthalmic invagination, ocular movement disorder, diplopia and ocular displacement, which seriously affects the function and appearance. For orbital blowout fractures, surgery should be performed as soon as possible when the intraocular invagion is more than 2mm and the fracture area is larger as confirmed by CT. In the repair of orbital fracture, the commonly used artificial materials include hydroxyapatite artificial bone, porous polyethylene polymer synthetic materials, hydroxyapatite complex and titanium metal materials. For orbital repair implant material choice, ideal implant materials should have the following characteristics: good biological compatibility, easy to shape and placed in orbit wall defect parts, easily able to retain its shape support orbital contents so as to maintain normal eye position, can replace the missing of the orbital contents and enlarge the orbital cavity volume, volume CT enhancement to facilitate postoperative observation. Since titanium mesh is easy to shape and has good fixation, it has no sensitization, carcinogenesis and teratogenicity in contact with human body, and it can be well combined with bone tissue, epithelium and connective tissue, so it is the best metal material with biocompatibility.
Preformed Orbital Plates are designed from CT scan data. These plates consist of implants that closely approximate the topographical anatomy of the human orbital floor and medial wall and are intended for use in a selective craniomaxillofacial trauma. Preformed three-dimensional shape: Designed for minimal bending and cutting which reduces the amount of time needed to contour plate. Contoured plate edges: For easy plate insertion through skin incision and less interference between the plate and surrounding soft tissue. Segmented design:To customize plate size to address orbital topography and to maintain contoured plate borders with minimal sharp edges. Rigid zone:Restores the shape to the posterior orbital floor to help maintain the correct position of the globe. comprehensive solutions for orbital floor repair and reconstruction.
-
locking maxillofacial mini 120° arc plate
-
locking maxillofacial mini straight plate
-
maxillofacial trauma 2.0 self tapping screw
-
locking maxillofacial micro X plate
-
locking maxillofacial micro straight plate
-
locking maxillofacial mini 90° L plate